Progress in the detection of heavy metal ions in the environment by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
[ Instrument Network Instrument R & D ] Recently, Researcher Huang Xingjiu of Intelligent Institute and Researcher Zhao Annan of Anguang Institute cooperated to use low-energy pulsed (15mJ) laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy assisted by active controlled spark discharge and electrochemical enrichment to achieve water and soil Highly sensitive and stable detection of trace arsenic and mercury in samples. Related research results have been published in Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical.
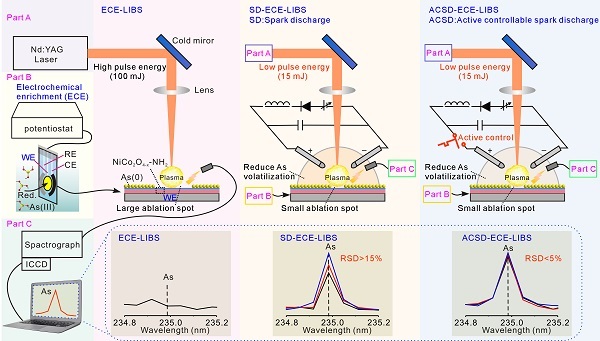
Figure: Schematic diagram of As (III) detection by electrochemical-LIBS equipment, spark discharge-electrochemical-LIBS equipment and active controllable spark discharge-electrochemical-LIBS equipment
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) has become a promising technology due to its unique advantages (such as multi-element analysis, fast response speed, no sample processing, and small sample damage), and is widely used in environmental samples. analysis. However, at high pulse energies, the detection of volatile traces of arsenic and mercury by LIBS faces great challenges. Compared with other heavy metals, arsenic and mercury are highly volatile, and their boiling points are 876K and 630K, respectively, while other heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Cu, Zn, Cr) have boiling points exceeding 1000K. In addition, at their boiling points, the calculated vapor pressures of arsenic and mercury are very high, several orders of magnitude higher than other heavy metal ions. Before the plasma signal is received, the arsenic and mercury detected with high pulse energy may have partially evaporated, resulting in ultra-high detection limits and even no signal of arsenic and mercury.
Based on the above problems, researchers have researched low-pulse energy LIBS with active controllable spark discharge and electrochemical enrichment to detect trace amounts of As (III) and Hg (II). The experimental results show that the low pulse energy laser reduces the volatilization of arsenic and mercury and reduces the ablation pits of the sample. The active controllable spark discharge device makes up for the problem of insufficient arsenic or mercury plasma content in the excited state caused by the low pulse energy laser. More importantly, researchers have added a controllable high-speed switch to the active controllable spark discharge device, and optimized the time between the spark discharge and the laser, thereby overcoming the instability of the traditional electric discharge-laser-induced breakdown spectrum The problem of stability was obtained with a stable plasma source. In addition, electrochemical enrichment of electrodes with modified flower-like NiCo2O4-x-NH2 nanosheets capable of regulating oxygen vacancies was achieved to achieve rapid and efficient enrichment of arsenic. As a result, this method shows high sensitivity (3.35 counts ppb-1), low detection limit (8.69 ppb), excellent stability (relative standard deviation is less than 5%) for detecting As (III), and also has Hg (II). Good detection effect.
This study uses a simple and easy-to-use method to achieve highly sensitive and stable detection of volatile As (III) and Hg (II) and hardly volatile heavy metal ions such as Cu (II). This will likely provide an effective analytical method for detecting heavy metal pollutants in the environment.
This research work was supported by key projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the innovative cross team of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, post-doctoral creative talents, major science and technology projects in Anhui Province, and the 13th Five-Year Plan of the National Key Program.
Scuba Diving Drysuits,Surfing Fitness Wetsuit,Men'S Surfing Wetsuit,Custom Surfing Fitness Wetsuit
Atenovo Garments(Yangzhou) Co.,Ltd. , https://www.neoklo.com